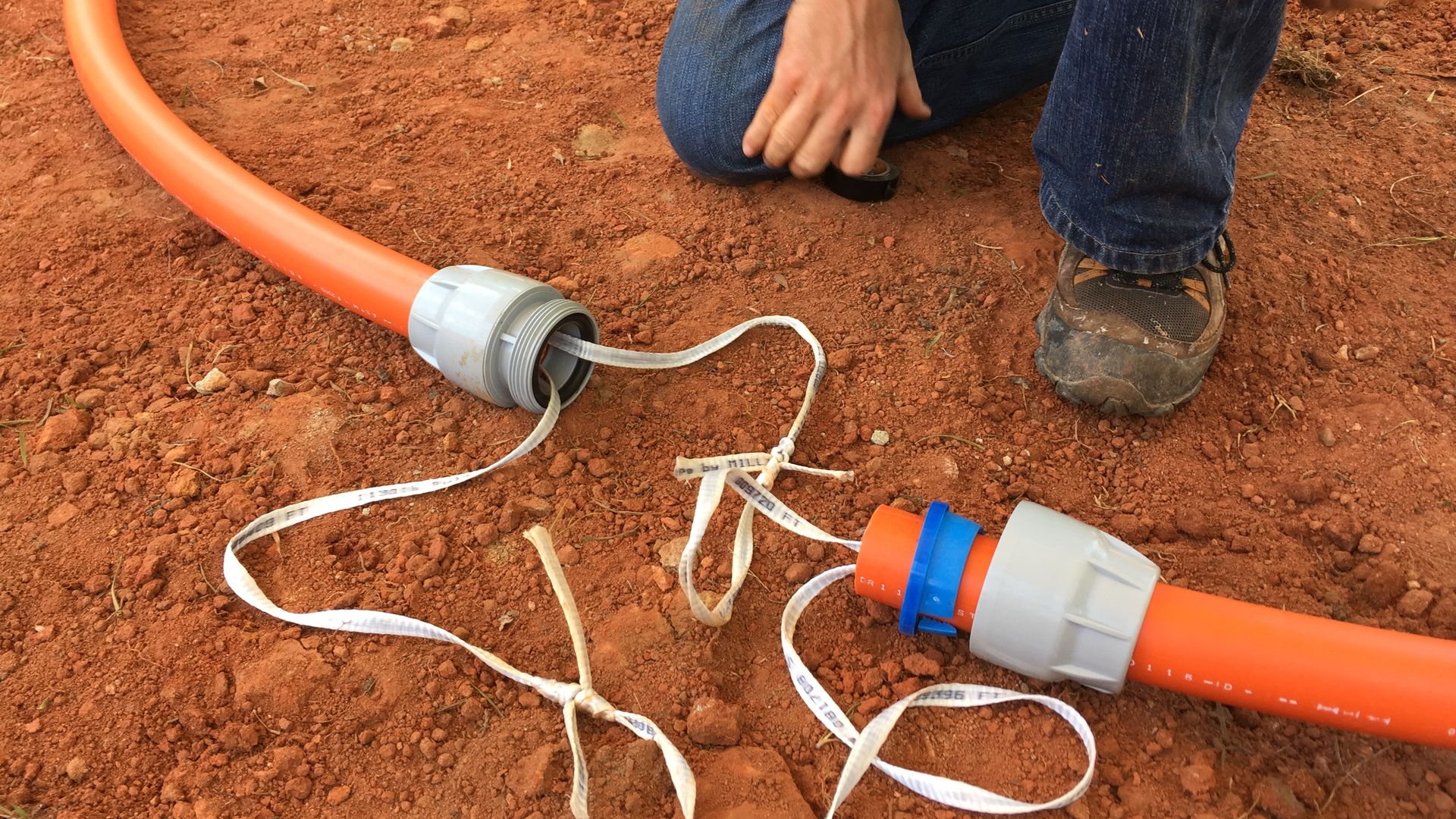
HDPE conduit is available in numerous configurations, lengths, colors, and with various features aimed at solving specific installation requirements. For example:
- Typically, conduit is provided in solid wall for OSP applications because of long lengths and stiffness, while corrugated conduit can be used for short OSP runs or ISP premise applications.
- Conduit can be color coded to allow easy end to end identification within a bundle.
- Multiple conduits can be packaged on a single reel allowing for multiple pathways to be installed simultaneously.
- Conduit can be provided in long continuous runs that minimize joints and facilitate faster installation.
- Conduit can be provided with:
– cable pre-installed during the conduit’s extrusion in the factory for a one-step field conduit/cable installation,
– a pull line, factory installed for field installation of the cable,
– inner wall ribs, lubrication, or both, lowering the coefficient of friction (COF) to facilitate longer cable installations,
– a tracer wire making the dielectric conduit locatable, and
– a high strength steel support strand for attaching to poles in aerial applications.
Solid or Corrugated Wall
Solid wall conduit is available in various standard wall thicknesses that can be matched to the application in order to assure the correct strength and toughness for installation and long-term service.
Corrugated innerduct, as shown in the figure, is flexible, lightweight and can be made of flame-retardant materials to be installed inside buildings (ISP) in accordance with the National Electrical Code (NEC).

Color Choices
While there are a number of color and stripe combinations available, single runs of conduit are typically colored red (or black w/longitudinal red stripes) for power, orange (or black w/longitudinal orange stripes) for communications, and terra cotta for CATV.
The various color schemes can also provide distinction amongst raceway owners, which is beneficial as it is common for multiple communication raceway owners to co-locate in the same trench.
If needed, special colors can be made available but minimum lengths may apply so consult with your HDPE conduit manufacturer for more details. There are three methods for providing color identification: full wall color, co-extruded exterior color, and longitudinal striping.
For longitudinal striping, the multiple stripes, typically 3 or 4, are co-extruded and placed at equally spaced intervals around the outside circumference of the conduit. For example, three stripes would be spaced at intervals of 120 degrees apart so as to optimize visibility when viewing from any direction.
The combination of solid and striping allows for many combinations that can be used to differentiate individual ducts within a bundle once installed.

Reel Packaging
Multiple ducts of different color/stripe combinations and sizes can be delivered on one common reel for a more efficient installation. Reels are wrapped in one of two manners: parallel wrapped with conduits re-spooled side-by-side or segment wrapped whereby the reel is compartmentalized for each color.
There are various reel designs, sizes and combinations available. Refer to the manufacturer’s literature for reel sizes options and capacity offerings.
Reduced Coefficient of Friction
Installation distances of the cable within the conduit can be limited by the friction between cable and conduit. Lowering the coefficient of friction (COF) results in less stress being placed on the cable during installation, which often allows for longer lengths of cable to be installed more efficiently.
Conduit can be provided with ribs and/or lubricated to improve cable installation distances. Conduit can be factory lubricated or lubricated in the field. Ribbed conduit (spiral or longitudinally) reduces friction and promotes turbulent airflow when installing cables using the push/blow method.

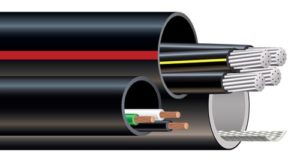
Cable in Conduit (CIC)
Cable in Conduit (CIC) is a conduit with cable factory installed providing time and labor savings by allowing one-step placement of both conduit/cable assembly. Cable in conduit can be provided with fiber, coaxial, twisted pair and electrical power cables already installed.
These cables are factory installed into the duct under controlled conditions, with thermal protection to ensure that the cable jacket is protected from the heat during conduit production. The integrity of the cable receives added protection during the field installation process from the surrounding HDPE duct.
Aerial Duct
Self-supporting duct, commonly known as Figure 8 Aerial Duct, incorporates an integral high strength steel strand in the assembly, used for suspension and support during and after aerial installation. Using aerial conduit with a factory assembled wire strand simplifies installation and eliminates the need for lashing.
The conduit assembly for both self-supported and lashed aerial installations must have an adequate level of UV protection, typically carbon black added to the HDPE resin during extrusion, to protect it from degradation during its anticipated service life.

Locatable Duct
Locatable duct has a copper wire extruded on the outside or within the conduit wall making it locatable. If digging is to be done in the area, a signal is placed on the tracer wire and the operator walks above the buried conduit using a location instrument to detect the signal.

Typically, the locator provides a readout of the burial depth and the operator will spray paint markings on the ground to indicate the buried conduit pathway underground.










